- Cognitive & Neuro
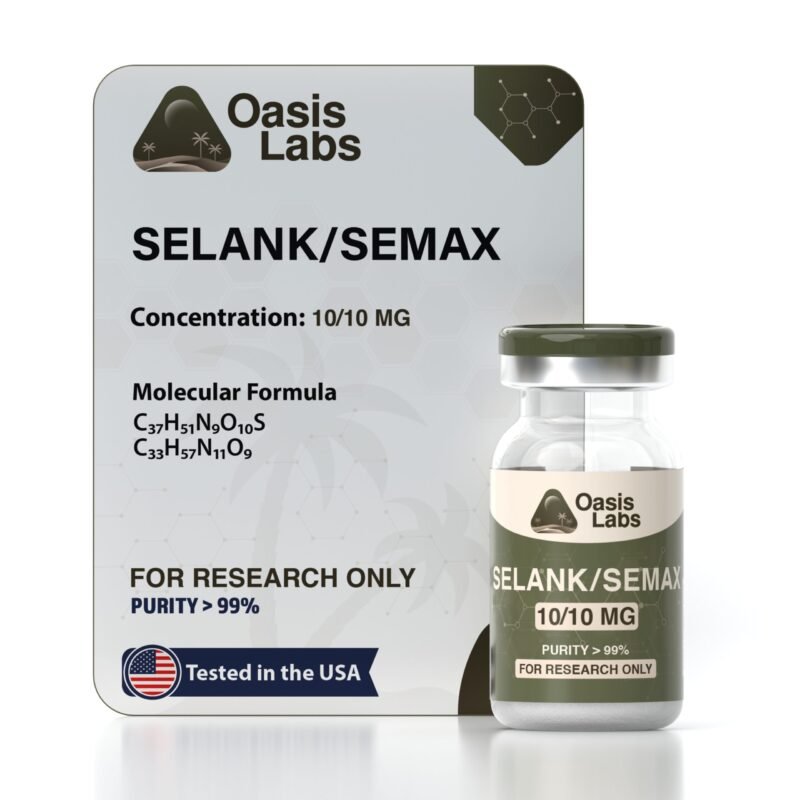
Selank / Semax 10/10mg Blend
Free Shipping on Orders Over $150!
Original price was: $134.00.$78.00Current price is: $78.00.
In stock
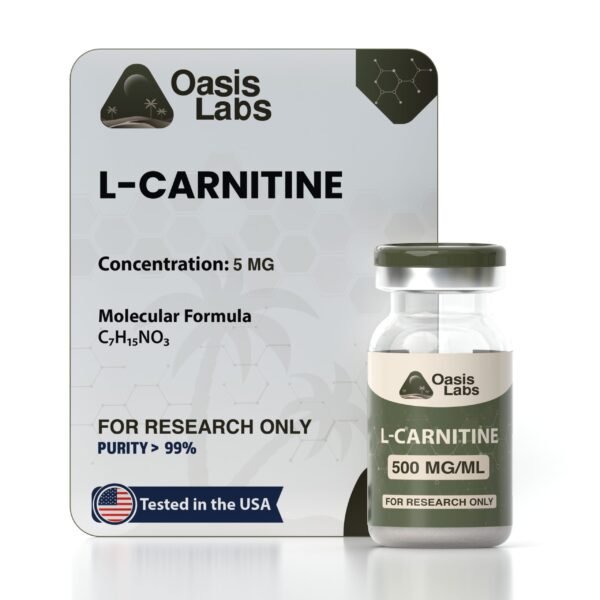
Product Name:
Selank / Semax Blend
Chemical Information:
-
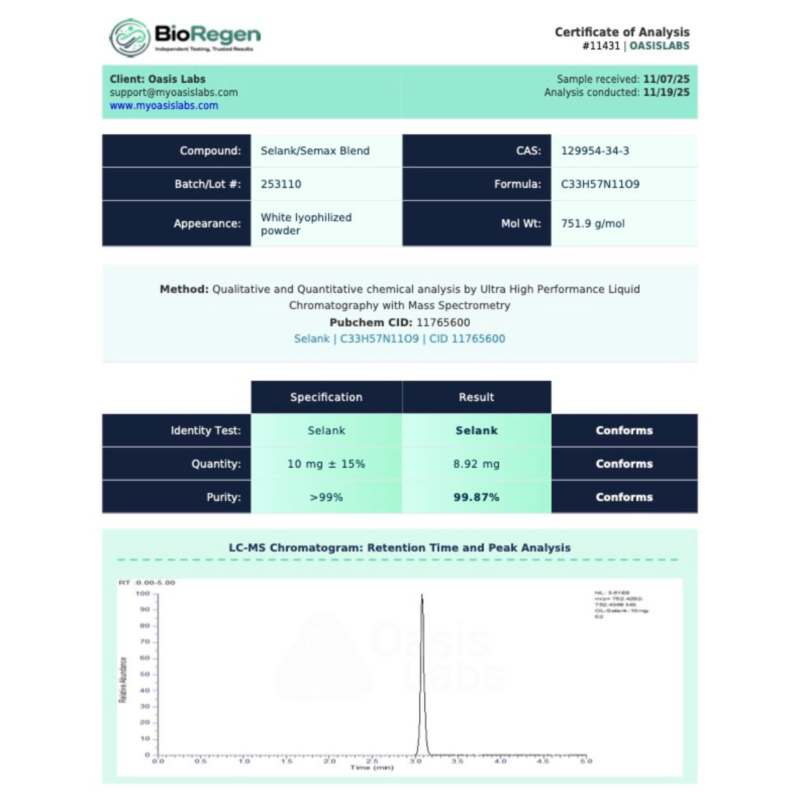
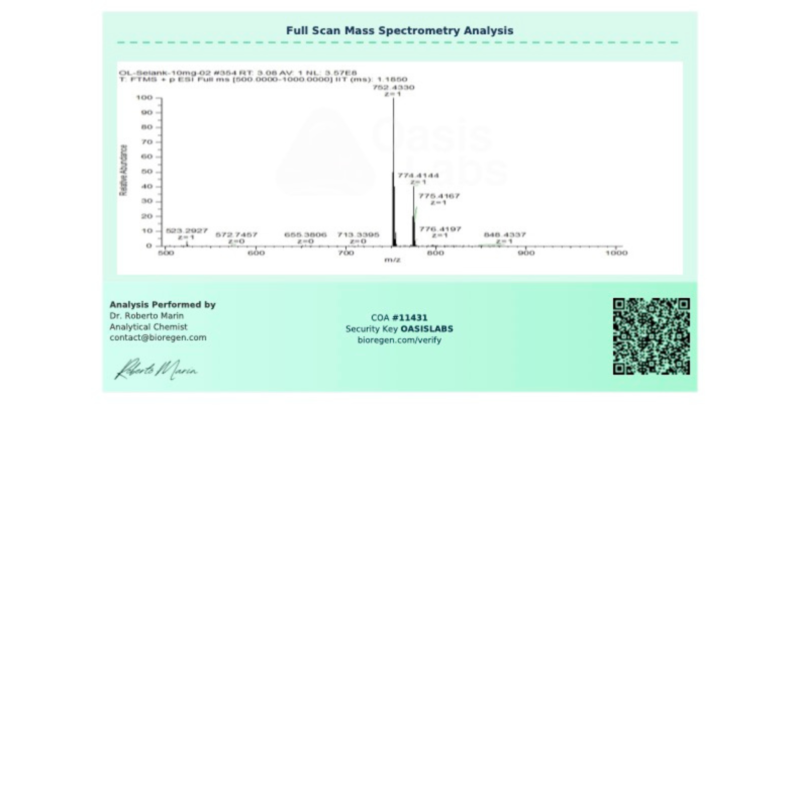
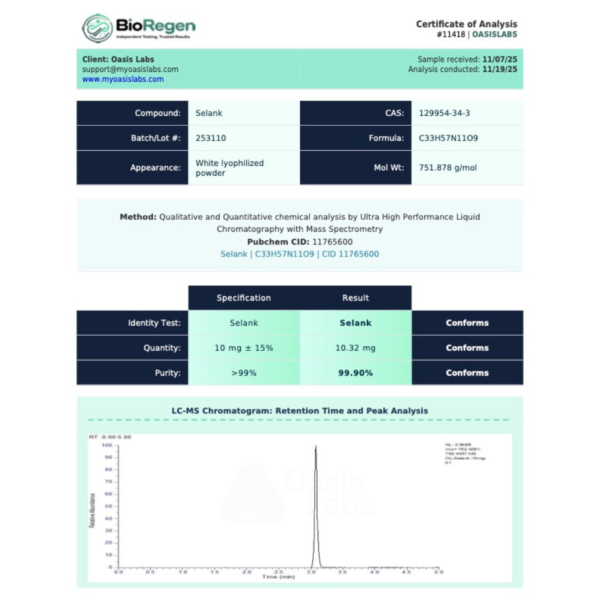
Selank Molecular Formula: C₃₃H₅₇N₁₁O₉
-
Selank Molecular Weight: 751.9 g/mol
-
Selank Sequence: Thr-Lys-Pro-Arg-Pro-Gly-Pro
-
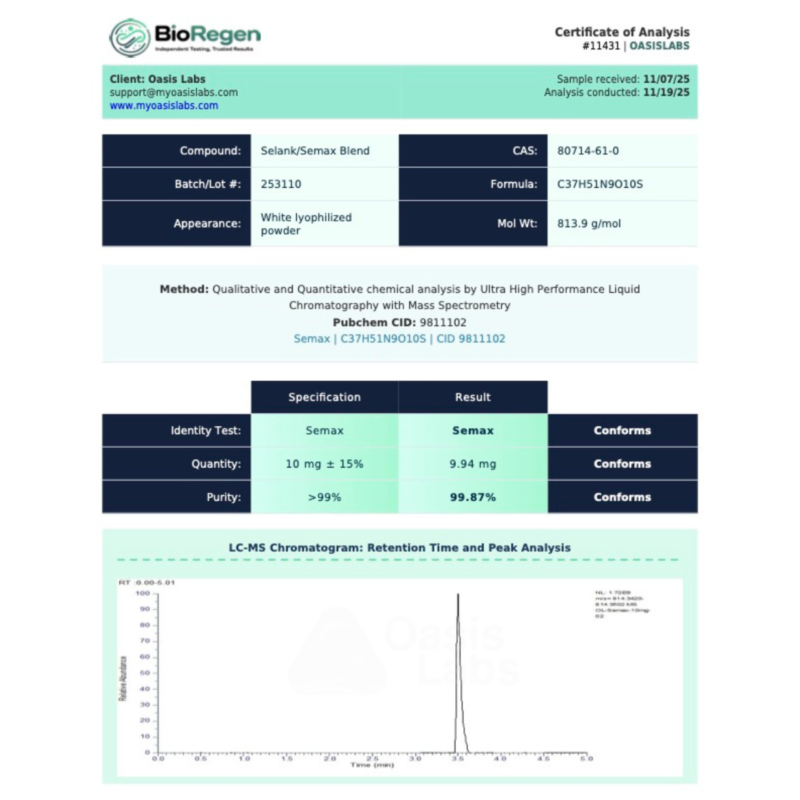
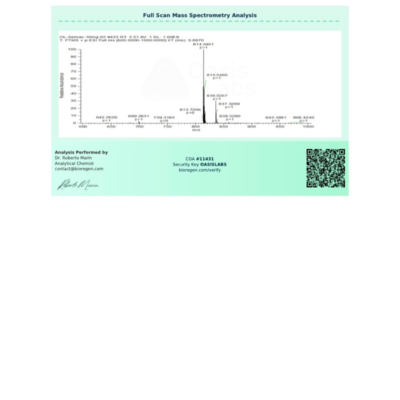
Semax Molecular Formula: C₃₇H₅₁N₉O₁₀S
-
Semax Molecular Weight: 813.93 g/mol
-
Semax Sequence: Met-Glu-His-Phe-Pro-Gly-Pro
-
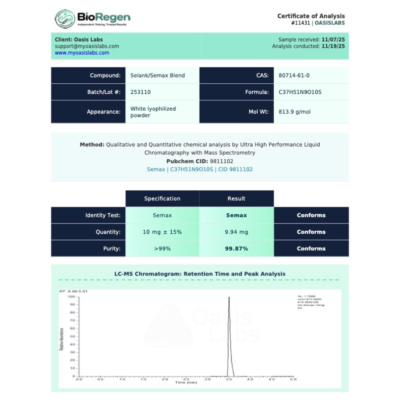
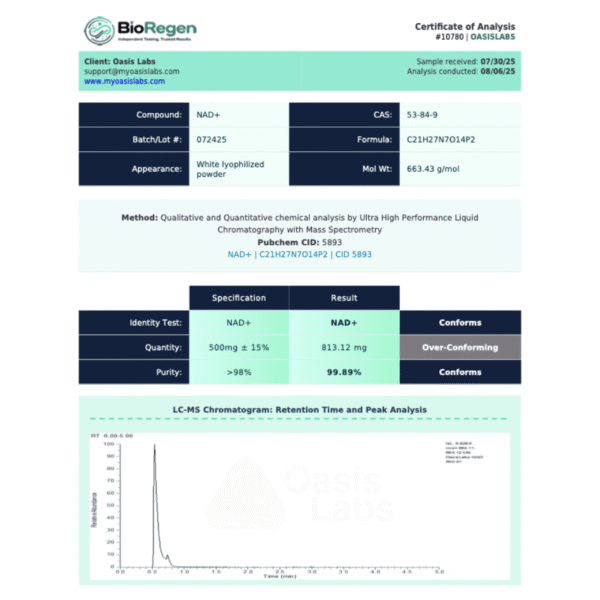
Molecular Structure: Refer to Certificate of Analysis for detailed structural information.
Storage and Handling:
-
Store sealed at recommended laboratory freezer temperatures.
-
Protect from light, moisture, and excessive heat.
-
Handle using standard laboratory safety procedures to maintain product integrity.
Product Specifications:
-
Purity: ≥99% (HPLC Verified)
-
Appearance: White to off-white lyophilized powder
-
Solubility: Refer to Certificate of Analysis for physicochemical properties
Important Note:
This product is strictly FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY and is intended exclusively for in vitro research and laboratory experimentation by qualified professionals. It is not a drug, food, cosmetic, or dietary supplement, and has not been evaluated by the FDA. This peptide is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. The bodily introduction into humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law. Any misuse, misbranding, or mislabeling is a violation of federal regulations and may result in legal action under applicable federal, state, or local laws.
References:
Referenced scientific publications include:
-
Ashmarin, I. P., et al. (2000). “Semax: A New Neuroprotective Peptide.” Neuroscience & Behavioral Physiology.
-
Myasoedov, N. F., et al. (2008). “The Role of Semax in Neuroprotection and Cognitive Enhancement.” Journal of Neurochemistry.
-
Medvedev, A. E., et al. (2005). “Neuropeptide Selank: Behavioral and Neurochemical Studies.” Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology.
-
Dolotov, O. V., et al. (2010). “Anxiolytic-Like Effects of Selank in Animal Models.” Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine.